How will 13 million farmers fight back against sea level rise?
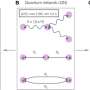
Researchers from the Institute for Environmental Sciences (IVM) at Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam have unveiled DYNAMO-M, a global agent-based model that projects how farmers across the world’s coasts may respond to the growing threat of coastal flooding and salt intrusion due to sea level rise (SLR). The model, which will be presented at the EGU General…